Sunday, November 27, 2011
Thursday, November 24, 2011
Meningitis
Meningitis is a bacterial infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord ( meninges ).

The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections that usually get better without treatment. However, bacterial meningitis infections are extremely serious, and may result in death or brain damage, even if treated.
Meningitis may also be caused by :
- Chemical irritation
- Drug allergies
- Fungi
- Tumors
Types include :
- Aseptic meningitis
- Cryptococcal meningitis
- Gram negative meningitis
- H. influenza meningitis
- Meningitis due to cancer ( carcinomatous meningitis )
- Meningococcal meningitis
- Pneumococcal meningitis
- Staphylococcal meningitis
- Syphilitic aseptic meningitis
- Tuberculous meningitis
Acute bacterial meningitis is a medical emergency, and requires immediate treatment in a hospital.
Viral meningitis is milder and occurs more often than bacterial meningitis. It usually develops in the late summer and early fall, and often affects children and adults under age 30. Most infections occur in children under age 5.
Most viral meningitis is due to enteroviruses, which are viruses that also can cause intestinal illness.
Many other types of viruses can cause meningitis. For example, viral meningitis can be caused by herpes viruses, the same virus that can cause cold sores and genital herpes ( although people with cold sores or genital herpes are not at a greater risk of developing herpes meningitis ).
Recently, West Nile virus, spread by mosquito bites, has become a cause of viral meningitis in most of the United States.
Symptoms usually come on quickly, and may include :
- Fever and chills
- Mental status changes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light ( photophobia )
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck ( meningismus )
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease :
- Agitation
- Bulging fontanelles
- Decreased consciousness
- Poor feeding or irritability in children
- Rapid breathing
- Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backwards ( opisthotonos )
Meningitis is an important cause of fever in children and newborns.
People cannot tell if they have bacterial or viral meningitis by how they feel, so they should seek prompt medical attention.
Physical examination will usually show :
- Fast heart rate
- Fever
- Mental status changes
- Stiff neck
For any patient who is suspected of having meningitis, it is important to perform a lumbar puncture ( "spinal tap" ), in which spinal fluid ( known as cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF ) is collected for testing.
Tests that may be done include :
- Blood culture
- Chest x-ray
- CSF examination for cell count, glucose, and protein
- CT scan of the head
- Gram stain, other special stains, and culture of CSF
Doctors prescribe antibiotics for bacterial meningitis. The type will vary depending on the bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics are not effective in viral meningitis.
Other medications and intravenous fluids will be used to treat symptoms such as brain swelling, shock, and seizures. Some people may need to stay in the hospital, depending on the severity of the illness and the treatment needed.
Early diagnosis and treatment of bacterial meningitis is essential to prevent permanent neurological damage. Viral meningitis is usually not serious, and symptoms should disappear within 2 weeks with no lasting complications.
Possible complication
- Brain damage
- Buildup of fluid between the skull and brain ( subdural effusion )
- Hearing loss
- Hydrocephalus
- Seizures
If you think that you or your child has symptoms of meningitis, get emergency medical help immediately. Early treatment is key to a good outcome.
Prevention
- Haemophilus vaccine ( HiB vaccine ) in children will help prevent one type of meningitis.
- The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is now a routine childhood immunization and is very effective at preventing pneumococcal meningitis.
- Household members and others in close contact with people who have meningococcal meningitis should receive preventive antibiotics to avoid becoming infected themselves.
The meningococcal vaccination is recommended for :
- Adolescents ages 11 - 12 and adolescents entering high school (about age 15) who have not already received the vaccination.
- All college freshmen who have not been vaccinated and are living in dorms.
- Children age 2 and older who do not have their spleen or who have other problems with their immune system.
- Those traveling to countries where diseases caused by meningococcus are very common (ask your doctor).

Wednesday, November 23, 2011
Hemophilia
What Is Hemophilia ?
Hemophilia ( heem-o-FILL-ee-ah ) is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood doesn't clot normally.
If you have hemophilia, you may bleed for a longer time than others after an injury. You also may bleed inside your body ( internally ), especially in your knees, ankles, and elbows. This bleeding can damage your organs and tissues and may be life threatening.

Overview
Hemophilia usually is inherited. " Inherited ” means that the disorder is passed from parents to children through genes.
People born with hemophilia have little or no clotting factor. Clotting factor is a protein needed for normal blood clotting. There are several types of clotting factors. These proteins work with platelets to help the blood clot.
Platelets are small blood cell fragments that form in the bone marrow ( a sponge - like tissue in the bones ). Platelets play a major role in blood clotting. When blood vessels are injured, clotting factors help platelets stick together to plug cuts and breaks on the vessels and stop bleeding.
The two main types of hemophilia are A and B. If you have hemophilia A, you're missing or have low levels of clotting factor VIII ( 8 ). About 9 out of 10 people who have hemophilia have type A. If you have hemophilia B, you're missing or have low levels of clotting factor IX ( 9 ).
Rarely, hemophilia can be acquired. " Acquired ” means you aren't born with the disorder, but you develop it during your lifetime. This can happen if your body forms antibodies ( proteins ) that attack the clotting factors in your bloodstream. The antibodies can prevent the clotting factors from working.
Outlook
Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on how much clotting factor is in your blood. About 7 out of 10 people who have hemophilia A have the severe form of the disorder.
People who don't have hemophilia have a factor VIII activity of 100 percent. People who have severe hemophilia A have a factor VIII activity of less than 1 percent.
Hemophilia usually occurs in males ( with rare exceptions ). About 1 in 5,000 males are born with hemophilia each year.

Thursday, November 17, 2011
Atelectasis
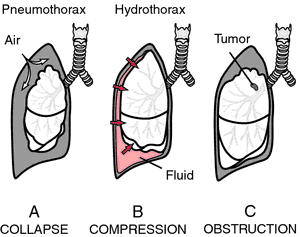
Atelectasis is the collapse of part or ( much less commonly ) all of a lung.

Atelectasis is caused by a blockage of the air passages ( bronchus or bronchioles ) or by pressure on the outside of the lung.
It is common after surgery, or in patients who were in the hospital.
Risk factors for developing atelectasis include :
- Anesthesia
- Foreign object in the airway ( most common in children )
- Lung diseases
- Mucus that plugs the airway
- Pressure on the lung caused by a buildup of fluid between the ribs and the lungs ( called a pleural effusion )
- Prolonged bed rest with few changes in position
- Shallow breathing ( may be caused by painful breathing )
- Tumors that block an airway
SYMPTOMS
- Breathing difficulty
- Chest pain
- Cough
TREATMENT
The goal of treatment is to re-expand the collapsed lung tissue. If fluid is putting pressure on the lung, removing the fluid may allow the lung to expand.
The following are treatments for atelectasis :
- Clap ( percussion ) on the chest to loosen mucus plugs in the airway
- Perform deep breathing exercises ( with the help of incentive spirometry devices )
- Remove or relieve any blockage by bronchoscopy or another procedure.
- Tilt the person so the head is lower than the chest ( called postural drainage ). This allows mucus to drain more easily.
- Treat a tumor or other condition, if there is one
- Turn the person to lie on the healthy side, allowing the collapsed area of lung to re-expand
- Use aerosolized respiratory treatments ( inhaled medications ) to open the airway
- Use other devices that help increase positive pressure in the airways and clear fluids ( positive and expiratory pressure [ PEP ] devices )
PREVENTION
Measures to prevent atelectasis are related to the various causes. They include :
- If you smoke, stop.
- If you are obese, lose weight.
- If you have a chronic lung or heart condition, follow your doctor's advice for managing the disease and limiting complications.
- If you are pregnant, get prenatal care and follow your doctor's instructions.
- Try not to inhale something solid. For example, chew your food well before swallowing.
- After surgery, follow instructions for deep breathing, coughing, and turning. Ask for pain medication if discomfort is limiting movement or coughing.
Monday, November 14, 2011
Conception To Birth
Conception is a small miracle - a matter of chance - and the length of time it takes to conceive a baby varies enormously. Some will be lucky and fall pregnant at the first attempt; others will still be trying a year or more later.
Now the real miracle begins ...
The egg will be fertilised within about 24 hours of its release. The genetic material from the sperm combines with the genetic material in the egg to create a new cell that will rapidly start dividing. You're not actually pregnant until that bundle of new cells, known as the embryo, travels the rest of the way down the fallopian tube and attaches itself to the wall of your uterus.
However, you can have an ectopic pregnancy if the embryo implants somewhere other than the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. An ectopic pregnancy is not viable, and the embryo has to be surgically removed to prevent rupture and damage to the fallopian tube.
That final leg of the trip, from fallopian tube to uterus, can take another three days or so, but it will be a couple of weeks until you miss a period and suspect that you're going to have a baby. Once you have missed your period or noticed one of the other signs of pregnancy, you can use a home pregnancy test to find out for sure if you've got a little one on the way. If so, congratulations, and welcome to the start of another incredible journey.
Sunday, November 13, 2011
Human Eye
The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye ( the part you see in the mirror ) includes :
- The iris ( the pigmented part )
- The cornea ( a clear dome over the iris )
- The pupil ( the black circular opening in the iris, which lets light in )
- The sclera ( the white part )
- The conjunctiva (an invisible, clear layer of tissue covering the front of the eye, except the cornea)
Just behind the iris and pupil lies the lens, which helps to focus light on the back of the eye. Most of the eye is filled with a clear gel, called the vitreous.
Light projects through the pupil and the lens to the back of the eye. The inside lining of the eye is covered by special light-sensing cells, together called the retina.
The retina converts light into electrical impulses. Behind the eye, the optic nerve carries these impulses to the brain.
The macula is a small sensitive area within the retina that gives central vision. It is located in the center of the retina and contains the fovea.
Eye color is created by the amount and type of pigment in the iris. Multiple genes inherited from each parent determine a person’s eye color.
Eye Conditions
Age-related macular degeneration : A loss of central vision in both eyes.
Myopia ( nearsightedness) : Inability to see clearly at a distance. The eye is “too long” for the lens, so light isn’t focused properly on the retina.
Hyperopia ( farsightedness ) : Inability to see near objects clearly. The eye is “too short” for the lens, or certain eye muscles have weakened with age.
Strabismus : The eyes do not point in the same direction. The brain may then favor one eye, causing decreased vision (amblyopia) in the other eye.
Pterygium : A thickened conjunctival mass usually on the inner part of the eyeball. It may cover a part of the cornea, causing vision problems.
Scotoma : A blind or dark spot in the visual field.
Amblyopia ( lazy eye ) : One eye sees better than the other, a problem of childhood development. The weaker eye may or may not “wander.” The weaker eye is called the " lazy eye ".
Astigmatism : A defect that causes an inability to properly focus light onto the retina. Astigmatism causes blurry vision that can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Cataract : A clouding of the lens, which hinders the passage of light through the lens.
Conjunctivitis : Also known as " pinkeye,” conjunctivitis is an infection or inflammation of the conjunctiva. It is usually caused by allergies, a virus, or a bacterial infection.
Glaucoma : Increased pressure inside the eye slowly reduces vision. Peripheral vision is lost first, often going undetected for years.
Diplopia ( double vision ) : Seeing double can be caused by many serious conditions. Diplopia requires immediate medical attention.
Retinal detachment : The retina comes loose from the back of the eye. Trauma and diabetes are common causes of this medical emergency.
Diabetic retinopathy : High blood sugar damages blood vessels in the eye. Eventually, weakened blood vessels may overgrow the retina or bleed, threatening vision.
Stye : Bacteria infect the skin on the edge of the eyelid, creating a tender red bump.
Chalazion : An oil-making gland gets blocked and swells into a bump. Often confused with styes, chalazions are not caused by infections.
Hyphema : Bleeding into the front of the eye, behind the cornea. Hyphema is usually caused by trauma.
Blepharitis : Inflammation of the eyelids near the eyelashes. Blepharitis is a common cause of itching or a feeling of grit in the eyes.
Corneal abrasion : A scratch on the clear part of the front of the eye. Pain, light sensitivity, or a feeling of grit in the eye are the usual symptoms.
Keratitis : Inflammation or infection of the cornea. Keratitis typically occurs after germs enter a corneal abrasion.
Retinitis : Inflammation or infection of the retina. Retinitis may be a long-term genetic condition or result from a viral infection.
Uveitis ( iritis ) : The colored part of the eye becomes inflamed or infected. An overactive immune system, bacteria, or viruses can be responsible.
Dry eye : Either the eyes don’t produce enough tears, or the tears are of poor quality. Dry eye can be caused by medical problems such as lupus, scleroderma, and Sjogren's syndrome.
Optic neuritis : The optic nerve becomes inflamed, usually from an overactive immune system. Painful vision loss in one eye typically results.
Black eye : Swelling and discoloration around the eye as a result of injury to the face.
Stroke
A stroke happens when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a " brain attack ".
If blood flow is stopped for longer than a few seconds, the brain cannot get blood and oxygen. Brain cells can die, causing permanent damage.
There are two major types of stroke : ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain is blocked by a blood clot. This may happen in two ways :
- A clot may form in an artery that is already very narrow. This is called a thrombotic stroke.
- A clot may break off from another place in the blood vessels of the brain, or from some other part of the body, and travel up to the brain. This is called cerebral embolism, or an embolic stroke.
Ischemic strokes may be caused by clogged arteries. Fat, cholesterol, and other substances collect on the artery walls, forming a sticky substance called plaque.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in part of the brain becomes weak and bursts open, causing blood to leak into the brain. Some people have defects in the blood vessels of the brain that make this more likely.
STROKE RISK FACTORS
High blood pressure is the number one risk factor for strokes. The other major risk factors are :
- Artrial fibrillation
- Diabetes
- Family history of stroke
- High cholesterol
- Increasing age, especially after age 55
People who have heart disease or poor blood flow in their legs caused by narrowed arteries are also more likely to have a stroke.
The chance of stroke is higher in people who live an unhealthy lifestyle by :
- Being overweight or obese
- Drinking heavily
- Eating too much fat or salt
- Smoking
OVERWEIGHT
Birth control pills can increase the chances of having blood clots. The risk is highest in woman who smoke and are older than 35.
The symptoms of stroke depend on what part of the brain is damaged. In some cases, a person may not know that he or she has had a stroke.
Symptoms usually develop suddenly and without warning. Or, symptoms may occur on and off for the first day or two. Symptoms are usually most severe when the stroke first happens, but they may slowly get worse.
A headache may occur, especially if the stroke is caused by bleeding in the brain. The headache :
- Starts suddenly and may be severe
- Occurs when you are lying flat
- Wakes you up from sleep
- Gets worse when you change positions or when you bend, strain, or cough
Other symptoms depend on how severe the stroke is and what part of the brain is affected. Symptoms may include :
- Change in alertness ( including sleepiness, unconsciousness, and coma )
- Changes in hearing
- Changes in taste
- Changes that affect touch and the ability to feel pain, pressure, or different temperatures
- Clumsiness
- Confusion or loss of memory
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty writing or reading
- Dizziness or abnormal feeling of movement ( vertigo )
- Lack of control over the bladder or bowels
- Loss of balance
- Loss of coordination
- Muscle weakness in the face, arm, or leg ( usually just on one side )
- Numbness or tingling on one side of the body
- Personality, mood, or emotional changes
- Problems with eyesight, including decreased vision, double vision, or total loss of vision
- Trouble speaking or understanding others who are speaking
- Trouble walking
A complete exam should be done.
- Check for problems with vision, movement, feeling, reflexes, understanding, and speaking. Your doctor and nurses will repeat this exam over time to see if your stroke is getting worse or improving.
- Listen for an abnormal sound, called a " bruit ", when using a stethoscope to listen to the carotid arteries in the neck. A bruit is caused by abnormal blood flow.
- Check your blood pressure, which may be high.
Tests can help your doctor find the type, location, and cause of the stroke and rule out other disorders.
- Angiogram of the head can show which blood vessel is blocked or bleeding
- Carotid duplex ( ultrasound ) can show if the carotid arteries in your neck have narrowed
- CT scan of the brain is often done soon after symptoms of a stroke begin. An MRI scan of the brain may be done instead or afterwards
- Echocardiogram may be done if the stroke could have been caused by a blood clot from the heart
- Magnetic resonance angiography ( MRA ) or CT angiography may be done to check for abnormal blood vessels in the brain
Other tests include :
- Lab tests will include :
- Bleeding time
- Blood cholesterol and sugar
- Blood clotting tests ( prothrombin time or partial thromboplastin time )
- Complete blood count ( CBC )
- Electrocardiogram ( ECG ) and heart rhythm monitoring -- to show whether an irregular heartbeat ( such as atrial fibrillation ) caused the stroke
A stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment can save lives and reduce disability.
It is very important for people who are having stroke symptoms to get to a hospital as quickly as possible. If the stroke is caused by a blood clot, a clot-busting drug may be given to dissolve the clot.
Most of the time, patients must reach a hospital within 3 hours after symptoms begin. Some people may be able to receive these drugs for up to 4 - 5 hours after symptoms begin.
Treatment depends on how severe the stroke was and what caused it. Most people who have a stroke need to stay in a hospital.
POSSIBLE COMPLICATION
- Breathing food into the airway ( aspiration )
- Dementia
- Falls
- Loss of mobility
- Loss of movement or feeling in one or more parts of the body
- Muscle spasticity
- Poor nutrition
- Pressure sores
- Problems speaking and understanding
- Problems thinking or focusing
Friday, November 4, 2011
Thursday, November 3, 2011
Sakit Dan Hikmahnya
Rasulullah pernah mengatakan, “ Aku mengagumi seorang mukmin karena selalu ada kebaikan dalam setiap urusannya. Jika ia mendapatkan kesenangan, ia bersyukur ( kepada Allah ) sehingga di dalamnya ada kebaikan. Jika ditimpa musibah, ia berserah diri ( dan menjalankannya dengan sabar ) bahwa di dalamnya ada kebaikan pula ”. ( HR Muslim )
Syukur ketika mendapatkan kebaikan / kesenangan adalah sesuatu yang mudah untuk dilakukan tetapi sabar ketika mendapatkan musibah adalah sesuatu sangat sukar untuk dilakukan. Keadaan itulah yang akan membezakan tahap keimanan seseorang. Semakin besar ujian yang diterima dan dia dapat bersabar maka semakin tinggilah darjat seseorang itu.
Salah satu ujian kesabaran bagi seorang muslim adalah sakit. Sakit yang menimpa seseorang itu memiki banyak hikmah, diantaranya :
1. Sakit adalah penggugur dosa-dosa hamba-Nya. Penyakit yang diderita seorang hamba menjadi sebab diampuninya dosa yang telah dilakukan termasuk dosa-dosa setiap anggota tubuh. Rasulullah s.a.w bersabda, “ Setiap getaran pembuluh darah dan mata adalah kerana dosa. Sedangkan yang dihilangkan Allah SWT dari perbuatan itu lebih banyak lagi ".
( HR. Tabrani ).
2. Orang sakit yang boleh bersabar akan mendapatkan pahala dan ditulis untuknya bermacam-macam kebaikan dan ditinggikan darjatnya. Rasulullah s.a.w bersabda, “
Tiadalah tertusuk duri atau benda yang lebih kecil dari itu pada seorang Muslim, kecuali akan ditetapkan untuknya satu darjat dan dihapuskan untuknya satu kesalahan" . ( HR. Muslim dari Aisyah ra ).
3. Sebagai balasannya, ia akan selamat dari seksa neraka. “ Aisyah Ummul Mukminin menerangkan sabda Rasulullah s.a.w bahawasanya sakit kerana demam itu akan menghindarkan orang Mukmin dari siksa api neraka ”. ( HR. Al-Bazzar )
4. Selalu ingat pada Allah SWT. Apabila di timpa musibah dan sakit akan membuat seseorang itu merasakan dirinya benar-benar lemah, tidak berdaya sehingga ia akan bersungguh-sungguh memohon perlindungan kepada Allah SWT. Dzat yang mungkin telah ia abaikan selama ini. Kepasrahan kepada Allah SWT ini pula akan memimpinnya untuk bertaubat.
5. Selalu mengingat nikmat Allah SWT. Sakit membuat seseorang itu memahami erti dan pentingnya kesihatan.
6. Pembersihan hati dari penyakit. Pendapat Ibnu Qayyim, “ Kalau manusia itu tidak pernah mendapat cubaan dan dugaan dengan sakit dan pedih, maka ia akan menjadi manusia ujub dan takabur. Hatinya menjadi kasar dan jiwanya beku. Musibah dalam bentuk apapun adalah rahmat Allah SWT yang disiramkan kepadanya. Akan membersihkan jiwanya dan menyucikan ibadahnya. Itulah ubat dan penawar kehidupan yang diberikan Allah SWT untuk setiap orang beriman. Ketika ia menjadi bersih dan suci kerana penyakitnya, maka martabatnya akan diangkat dan jiwanya akan dimuliakan. Pahalanya pun berlimpah-limpah apabila penyakit yang menimpa dirinya diterimanya dengan sabar dan redha ”.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)









































